We all are aware of Google’s integration of its Gemini AI model directly into the Chrome browser. Dubbed “Gemini in Chrome,” this feature allows users to request key insights, clarifications, or tasks based upon the current page without switching tabs or leaving the browser window. For example, Gemini can generate summaries, suggest follow-up questions, and operate across multiple open tabs to consolidate information.
Looking ahead, it also promises agentic browsing, enabling the AI to carry out user tasks, such as making bookings or placing orders, fully inside the browser environment.
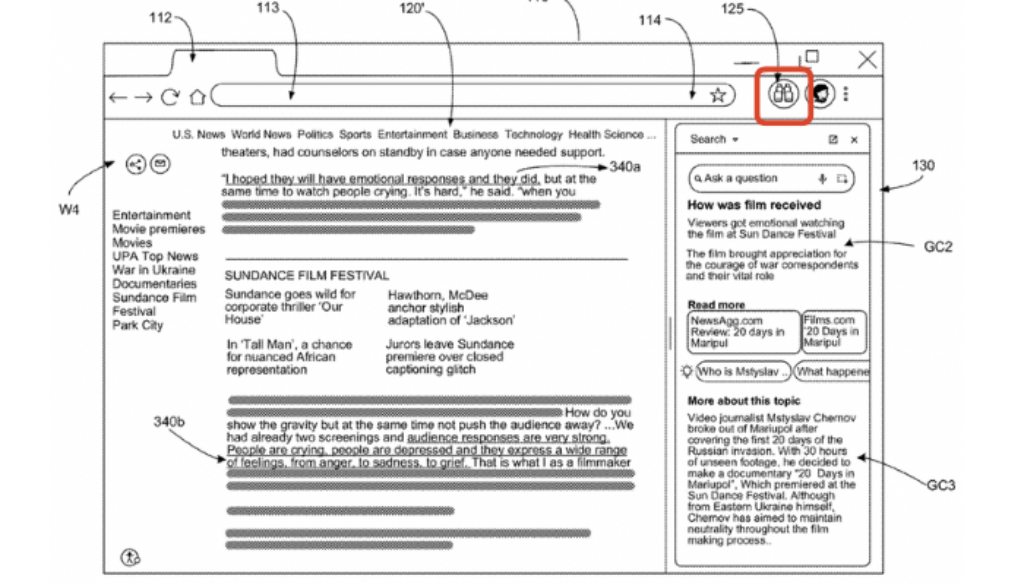
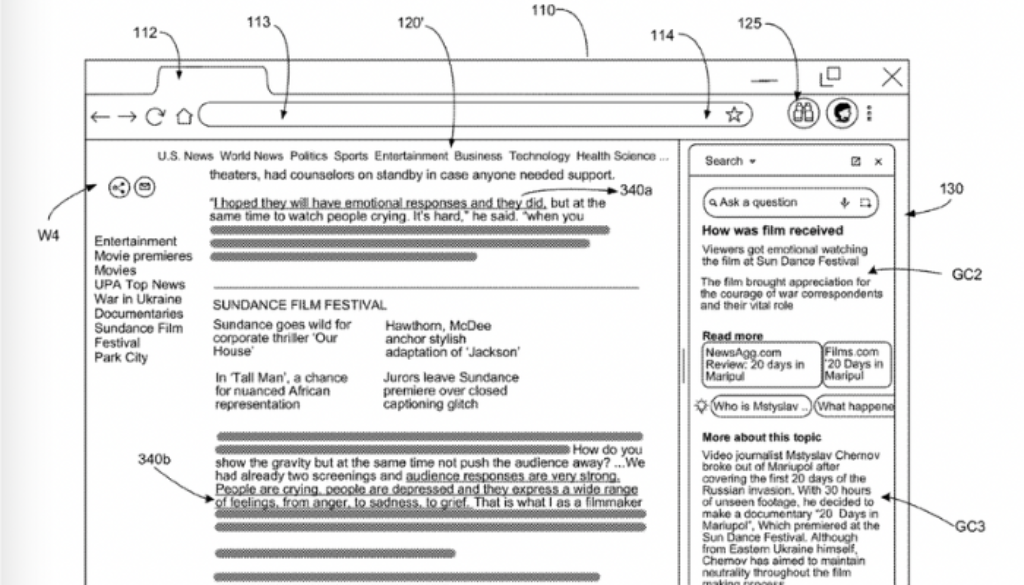
The new patent document by Google aligns closely with this emerging paradigm. It describes a browser-integrated contextual search tool – a system that extracts core content from a primary resource and displays contextual suggestions, summaries, or AI-generated content in a side panel or overlay, all without forcing the user to navigate away. That is, the patent formalizes a framework for the very kind of intelligence now being seen in real-world browsers like Chrome + Gemini.
By situating this patented architecture alongside current innovations, we see that the groundwork for intelligent, context-aware browsing is no longer speculative. It is actively being deployed. As browsers like Chrome evolve into AI assistants rather than mere viewers, the principles laid out in the patent serve as a meaningful blueprint for how content extraction, entity recognition, and generative augmentation can be integrated into the user experience.
What can it do?
When you’re browsing content (say reading a webpage), the tool can:
- Extract core content (text or elements from the page).
- Provide contextual suggestions in a side/search area.
- Show summaries or related info instantly.
- Use generative AI to create explanations, problem solutions, or summaries directly related to what you’re reading.
The contextual area is separate from the main content but still inside the browser, so the user doesn’t lose focus.
How will it work?
- Extract Content
- Pulls relevant parts of the webpage/document (core content).
- Identifies entities like names, places, products, etc.
- Generate Suggestions or Content
- Contextual search results (e.g., reviews, definitions, comparisons).
- Generated summaries (e.g., math solutions, topic explanations, draft responses).
- AI-powered expansions (like large language models producing related ideas).
- Display in Browser
- Suggestions or generated text are displayed in a contextual search area (side panel, box, or overlay).
- The main content remains open and visible.
Key Features of this new contextual search tool
- Non-intrusive: Doesn’t replace the main page, only adds a parallel search/info panel.
- Smart extraction: Uses document structure (like DOM parsing) to pick useful content.
- Entity-based: Can recognize entities (e.g., hotel names, product names) and fetch related info (prices, reviews, etc.).
- Generative AI integration: Uses LLMs to create summaries, draft explanations, or creative responses.
- Custom filtering: Can exclude irrelevant or sensitive data.
- UI flexibility: May appear as a side panel, pop-up, or embedded box in the browser.
Some of the practical references
- While reading a movie review, the tool can suggest:
- Cast details
- Related critic reviews
- Box office info
- While viewing a product page, it can suggest:
- Price comparisons
- Customer reviews
- Alternative products
- While working on homework problems, it can:
- Generate explanations or summaries (e.g., math solutions, essay outlines).
Why Contextual Browsing Matters?
- Saves time (no need to switch tabs or search manually).
- Enhances understanding with on-the-spot context.
- Supports both factual lookups and AI-generated content.
- Works on desktop browsers, mobile browsers, and possibly other apps.
We believe it’s a step forward by Google in how we interact with digital content. Instead of forcing users to jump between multiple tabs or conduct separate searches, the contextual search tool makes the browser itself smarter and more interactive. By combining content extraction, contextual suggestions, and AI-driven generation, it creates a seamless experience where information and insights are available instantly, in the same place where the user is already engaged.